Remittance providers can scale cross-border infrastructure more sustainably using Arrel’s modular API-based approach

A conceptual illustration of global remittance flows enabled by digital asset APIs, highlighting Africa and emerging markets as core connectivity hubs in modern financial infrastructure.
Arrel, an African digital asset infrastructure provider, announces modular APIs to address cost, pre-funding, and scalability challenges in remittances.
The APIs are intended for regulated and regulation-ready remittance startups and established remittance operators seeking to launch new corridors, optimize existing operations, or update cross-border payment infrastructure without adopting bundled, fixed-cost platform solutions.
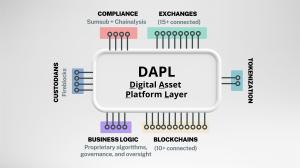
DAPL is designed for remittance operations that require multiple infrastructure components to operate across corridors and transaction volumes. Cross-border remittance services typically rely on a combination of liquidity access, compliance processes, treasury controls, and settlement mechanisms, each of which introduces operational and cost considerations as activity increases.
Within the DAPL architecture, remittance infrastructure is organized around the following core components, which are commonly required to launch or operate a remittance service from the outset:
- Access to liquidity in multiple currencies
- Connectivity to exchanges or liquidity providers
- Transaction monitoring and compliance tooling
- Treasury controls and settlement logic
- Local payout rails for each corridor
- A routing layer capable of executing across multiple liquidity venues through a single integration, without an internal order management system (OMS)
- Pre-funded accounts across multiple currencies and corridors, resulting in working capital allocation and FX and liquidity exposure
These components are commonly deployed through multiple service providers and involve separate commercial agreements, technical integrations, regulatory reviews, and operational workflows. In many cases, they are delivered as bundled enterprise offerings with fixed pricing structures, minimum volume commitments, and long-term contractual arrangements that apply independently of transaction activity.
In addition, remittance operations frequently maintain pre-funded balances across corridors and currencies as part of settlement and payout processes. This approach allocates capital across multiple markets and introduces FX and liquidity exposure as transaction volumes and corridor coverage increase.
DAPL was developed as a digital asset orchestration layer that separates these infrastructure components and exposes them through standardized APIs. Arrel was established in Mauritius to build this modular architecture and provide remittance operators with an alternative to single-stack, bundled infrastructure platforms.
Arrel’s APIs are organized around four core functional areas.
Function One: Liquidity and currency access
These APIs provide programmatic access to liquidity across multiple exchanges and liquidity providers through a single integration. Remittance operators can access settlement currencies such as USD, EUR, ZAR, XAF, XOF, as well as corridor-specific currencies where available. Stablecoins are supported as a settlement mechanism within the platform, alongside reconciliation and reporting processes.
Integrations include liquidity providers and venues such as Binance, Bitfinex, Bitstamp, [CEX.IO](http://cex.io/), LMAX, Deribit, [Gate.io](http://gate.io/), HTX, Indodax, Kraken, KuCoin, Luno, OKX, Poloniex, VALR, and Xago. Settlement is supported across multiple blockchains, including Arbitrum One, BNB Chain, Ethereum, Optimism, Polygon, Bitcoin, Stellar, and Tron. Custody is supported through Fireblocks and native MPC wallets, with compliance tooling integrated via Chainalysis for KYT and Sumsub for KYC and KYB.
Function Two: Compliance and transaction monitoring
These APIs provide compliance and transaction monitoring capabilities within remittance transaction flows. The APIs expose KYT, AML, and KYC or KYB checks, including screening outputs, risk indicators, and audit records. Compliance rules can be applied programmatically at the transaction level across supported corridors.
Function Three: Treasury and settlement orchestration
These APIs support the configuration of treasury wallets, approval policies, and settlement rules across connected venues. Available capabilities include balance monitoring, automated fund movements, FX exposure tracking, and policy-based approvals. Treasury configuration and execution are managed within a centralized orchestration layer.
Function Four: Local rails and corridor execution
These APIs support connectivity to regulated local partners for payouts and settlement into domestic banking and payment systems. Through integrations with licensed providers such as Xago, remittance operators can access local rails without establishing direct bilateral banking relationships for each corridor. Corridor connectivity can be extended by adding payout integrations while maintaining the same orchestration, monitoring, and audit framework.
Beyond banking and exchange connectivity, Arrel plans to extend the platform to support integrations with telecom operators and mobile money aggregators as an additional module. This would enable remittance workflows to interface with mobile-based payment systems in peri-urban and remote areas where traditional banking infrastructure may be limited.
In addition to individual APIs, Arrel offers modular infrastructure bundles built on top of these core functional areas. Operators can deploy a Core Remittance Bundle, which includes liquidity routing, compliance monitoring, and treasury orchestration, and add Corridor Bundles as needed. Each Corridor Bundle is associated with specific local payout rails and corridor requirements. Bundles are configured to support usage-based deployment rather than fixed platform commitments.
Under this model, corridor rollout is handled through incremental configuration. Each additional corridor typically involves integrating a new payout rail and applying local requirements, while the underlying liquidity, compliance, and treasury components remain unchanged.
Arrel is a member of the Circle Alliance, reflecting alignment with institutional stablecoin infrastructure standards. Together with regulated local partners such as Xago, the APIs are designed to operate within established financial, regulatory, and supervisory frameworks.
Through the use of modular APIs and configurable infrastructure bundles, Arrel provides remittance operators with an alternative deployment model for cross-border infrastructure. Infrastructure usage and capital allocation can be configured in relation to transaction activity rather than through fixed, bundled platform structures.
This modular deployment model supports corridor-by-corridor expansion and incremental infrastructure configuration. In African markets, where remittance corridors and payout mechanisms vary significantly, the approach allows operators to deploy services across different environments while maintaining a consistent orchestration and monitoring layer.
Editorial Team
tracee
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.